gas analysis by gc|german gas chromatography : wholesaling Agilent has developed a robust catalyst gas analysis by gas chromatography (GC) for use in the analysis of gases produced by carbon dioxide technologies. The GC incorporates a multidimensional design, using thermal conductivity and a flame ionization detector (FID) coupled with a nickel catalyst to provide analysis of hydrogen (H 2), oxygen (O 2 WEBCheating Wife Alana LOVES Showing Off To Her New Bull😈cucks KIK -Boredafhmu20 for proper treatment BullouttaNY. 1 99,7K. Alaninha Natal full videos: https://link .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webResultados. 1º 8768-17 — MACACO. 2º 6053-14 — GATO. 3º 5137-10 — COELHO. 4º 4094-24 — VEADO. 5º 5211-03 — BURRO. 6º 7132-08 — CAMELO. 7º 6850-13 — .
A Practical Gas Analysis by Gas Chromatography provides a detailed overview of the most important aspects of gas analysis by gas chromatography (GC) for both the novice and expert. Authors John Swinley and Piet de Coning provide the necessary information on the selection .GC is basically a gas analyzer the use of a general and sensitive µTCD for measuring the fixed gases is required. Hydrogen analysis with a TCD using helium carrier gas Normally, there are no strange occurrences in the thermal conductivities when mixing components, with the exception of helium-hydrogen mixtures [1]. As a result of their close Gas chromatography is widely used for the quantitative analysis of a diverse array of samples in environmental, clinical, pharmaceutical, biochemical, forensic, . In a GC analysis the area under the peak is .Agilent has developed a robust catalyst gas analysis by gas chromatography (GC) for use in the analysis of gases produced by carbon dioxide technologies. The GC incorporates a multidimensional design, using thermal conductivity and a flame ionization detector (FID) coupled with a nickel catalyst to provide analysis of hydrogen (H 2), oxygen (O 2
Analysis of Permanent Gases Sample Introduction –Syringes and valves General discussion on PLOT columns The molesieve column is at the heart of permanent gas separations Techniques when CO 2 + C 2’s, C 3’s, etc. is also needed Column Isolation Parallel columns Cryogenic separations Unique selectivity packed columns. in 1952. More than 60 years after the award, GC systems are widely commercialized and used in various industries, capable of both of quantitation and qualifcation. GC is applicable for many types of analysis in the markets such as residual solvent analysis in pharmaceuticals, residual pesticides analysis in food safety, trace level
Table 1 shows the typical GC conditions for impurities in 1,3-Butadiene analysis based on configuration B. Table 2 lists the gas standard mixtures used for method development. Table1. Typical GC Conditions for Impurities in 1,3-Butadiene Analysis Based on Configuration B with Backflushing Gas chromatograph Agilent 7890A Series GC In early 1900s, Gas chromatography (GC) was discovered by Mikhail Semenovich Tsvett as a separation technique to separate compounds. In organic chemistry, liquid-solid column chromatography is often used to separate organic compounds in solution. . The analysis begins at a low temperature to resolve the low boiling components and increases .
gemstone hardness tester
The saturate fraction is analyzed by gas chromatography, leading to n-alkanes content. Aromatics are analyzed by Gas Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Resins and asphaltenes are the most difficult to analyzed by GC because of their high boiling points. Therefore, the applications of GC on the analysis of heavy oil, which has a highcarrier gas. When using hydrogen as the carrier gas, try an initial average linear velocity of 60 cm/sec. If better resolution is desired, reduce the velocity to no less than 50 cm/sec; however, the analysis time will be increased. If a shorter analysis time is desired, increase the velocity to 70 cm/sec and 80 cm/sec. Betemperature of the gas will decrease as the pressure is reduced. Whereas the amount of cooling is dependent on the composition of the gas, a typical value used for estimating the cooling of natural gas is 7 °F per 100 PSI (American Gas Association, n.d.) or 5.6 °C per 1000 kPa. As the temperature of a hydrocarbon gas mixture is QUANTtitative Analysis. Quantitative analysis tells us how much of an analyte is in a mixture. In an ideal GC or GC-MS analysis, the peak height and area under the peak are proportional to the amount of analyte injected onto the column. A peak’s area is determined by integration, which usually is calculated by the instrument’s computer.
gas Analyzer by FPD ASTM D6228 Sulfur in gas fuels by SCD ASTM D5504 •For samples where it is not feasible to completely separate sulfur components from the hydrocarbon matrix and low ppb sensitivities are required, the SCD can be considered if experienced users are available. •A good detector for low-level sulfur,Example of a GC–MS instrument. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) is an analytical method that combines the features of gas-chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. [1] Applications of GC–MS include drug detection, fire investigation, environmental analysis, explosives investigation, food and flavor . Capillary Columns. A capillary, or open tubular column is constructed from fused silica and is coated with a protective polymer coating. Columns range from 15–100 m in length with an internal diameter of approximately 150–300 μm. Figure 12.4.3 shows an example of a typical capillary column.Gas chromatography (GC) is a common analytical technique used to separate and analyze volatile and semi-volatile compounds in a mixture. GC is a popular analytical technique as it combines exceptional resolving power with speed .
TDA-GC is used to separate and measure various types of gases from mixed gas components discharged from a sample 16,17.This qualitatively and quantitatively analyzes the corresponding gas by .
Quantitative Analysis. In a GC chromatogram, the size and area of the component peak are proportional to the amount of the component reaching the detector. . of changes in sample composition when introduced to a gas .
Gas chromatography is an ideal tool for analysis of gases. The versatility of the technique extends its capability to analyse samples such as dissolved solids, liquids and gases. . Improve reproducibility of syringe injections for GC analysis; Simple steps to minimize Column bleed from GC columns; Our Courses.Single quadrupole GC-MS. When gas chromatography is combined with a mass spectrometer that includes just one quadrupole, it is often referred to simply as GC-MS. GC-MS is well suited to the everyday analysis of samples where either targeted or untargeted analysis is required as these systems can be operated using either targeted selected ion monitoring (SIM) or . Recently a cutting-edge drilling technology has increased the use of shale gas. As the production area diversifies, the need for gas composition analysis has increased. Shimadzu addresses analytical requests with a wide system GC lineup. For analysis of liquified gas, such as LPG, a dedicated injector with a vaporizer is available.1.1. Overview of GC Analysis. Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique applicable to gas, liquid, and solid samples (components that are vaporized by heat). If a mixture of compounds is analyzed using GC system, each compound can be separated and quantified.
Single quadrupole GC-MS. When gas chromatography is combined with a mass spectrometer that includes just one quadrupole, it is often referred to simply as GC-MS. GC-MS is well suited to the everyday analysis of samples where either targeted or untargeted analysis is required as these systems can be operated using either targeted selected ion monitoring (SIM) or .
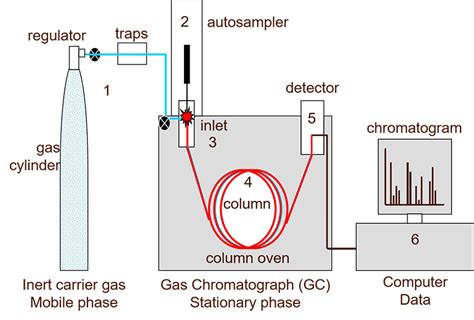
The new instrumentation specifically designed for GC water analysis (for example, columns, detectors, headspace samplers, and flow gas purifiers) make GC the first truly competitive and often superior approach to KFT. Its speed, accuracy, and ease of automation offer advantages that are difficult to match with KFT or other techniques.Gas chromatography is a traditional method used to separate organic compounds (de Jesus et al., 2020).It is a technique in which the gas phase analyte is transported through the column by a carrier gas (mobile phase), which can be He, N 2, or H 2 (Harris, 2005) (Fig. 2.6).This separation technique may occur by gas–solid adsorption, where the analyte is adsorbed by the solid . Today, a wide variety of techniques is available for the preparation of (semi-) solid, liquid and gaseous samples, prior to their instrumental analysis by means of capillary gas chromatography (GC) or, increasingly, comprehensive two-dimensional GC (GC × GC). In the past two decades, a large number of ‘modern’ sample-preparation techniques has been .
A major challenge to analysis of chlorine gas is the corrosive nature of chlorine, which is a strong oxidizer and will corrode system components. This gas chromatograph is constructed of corrosion resistant alloys or otherwise treated to minimize degradation. This application is available on the GC-2014 platform.
Uses of Gas Chromatography . GC is used as one test to help identify components of a liquid mixture and determine their relative concentration.It may also be used to separate and purify components of a mixture.Additionally, gas chromatography can be used to determine vapor pressure, heat of solution, and activity coefficients.Industries often use it to .
the first gas chromatography
16 de jul. de 2021 · As Prefeituras de Araras e Pirassununga lamentaram a morte do jornalista em postagens no site oficial e nas redes sociais. Veja a nota da prefeitura de Araras: A Prefeitura de Araras manifesta seu .
gas analysis by gc|german gas chromatography